radial nerve compression test|radial nerve special tests : wholesaling Radial Tunnel Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the posterior interosseous nerve (PIN) at the level of proximal forearm (radial tunnel). Diagnosis is made clinically with pain only (maximal tenderness 3-5 cm distal . Resultado da 14 de jan. de 2022 · Home Economics – 1ª Temporada (Home Economics, EUA, 7 de abril à 9 de maio de 2021) Criação: John Aboud, Michael Colton .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webO acesso aos Produtos Globo (Globoplay, Globoplay + canais ao vivo, Premiere, Combate, Cartola PRO, Telecine, Giga Gloob e Globo Mais) é realizado pela Conta Globo. Se .
Radial Tunnel Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the posterior interosseous nerve (PIN) at the level of proximal forearm (radial tunnel). Diagnosis is made clinically with pain only (maximal tenderness 3-5 cm distal . Radial Nerve. At the wrist, the superficial radial nerve is susceptible to injury by compression because it runs superficially to the flexor retinaculum. Radial nerve entrapment is an uncommon diagnosis that is prone to under-recognition. Compression or entrapment can occur at any location within the course of the .Radial Tunnel Syndrome is a syndrome resulting from the compression of the posterior interosseous nerve at the level of the proximal forearm. It does not present with any specific radiological or electrodiagnostic findings.
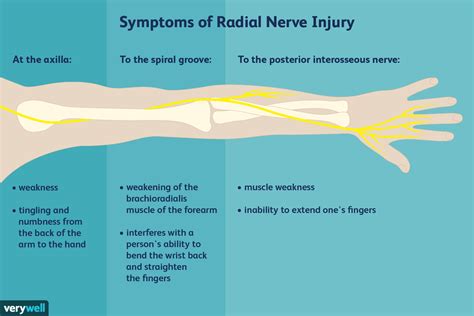
Radial nerve injury typically occurs due to compression, entrapment, traction, or direct trauma to the nerve, which causes a local inflammatory response with swelling and edema. Compressive .There is no single, clear test to diagnose the condition. The patient’s history and physical exam determine the diagnosis. Figure 1. The radial nerve, one of the five major nerves in the upper .Radial tunnel syndrome (RTS) develops from intermittent compression of the radial nerve in the structure known as the radial tunnel, leading to pain on the antebrachial dorsum without . In some cases, you might have a test called electromyography (EMG). An EMG lets doctors see how well your muscles and nerves are working, including your radial nerve.
Radial tunnel syndrome is compression of the radial nerve in the proximal forearm. Symptoms include forearm and elbow pain. Diagnosis is clinical. Treatments include splinting and .Radial tunnel syndrome is caused by a pinched nerve, called the radial nerve, that runs through the muscles on the top of the elbow and forearm. . clear test to diagnose the condition. The patient’s history and physical exam determine the diagnosis. Figure 1. The radial nerve, one of the five major nerves in the upper extremity, runs . Radial tunnel syndrome refers to a rare compressive neuropathy of the posterior interosseous nerve (PIN) as it passes through the radial tunnel resulting in pain without motor or sensory dysfunction.[1] This pain-only phenomenon is contrasted with PIN compression syndrome, which describes a more severe PIN compressive neuropathy, ultimately causing .
Nerve compression syndromes of the hand present with various signs and symptoms that correspond to the nerve involved and its anatomic distribution. There are three nerves and their corresponding branches that .A nerve conduction study is a diagnostic test that evaluates the function of your peripheral nerves. It’s a type of electrodiagnostic test. . such as peripheral neuropathy and nerve compression syndromes. Healthcare providers often use this test alongside an EMG (electromyography) test. . Radial tunnel syndrome. Thoracic outlet syndrome. Middle finger test - Reproduction of radial nerve pain during resisted middle finger extension suggests compression of the radial nerve by the extensor carpi radialis brevis.This test may also be positive in lateral epicondylitis, but radial tunnel irritation is the likely diagnosis when this test is more painful than passively flexing the fingers and wrist of an .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. Tinel's test is used to test for compression neuropathy, commonly in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome.. Technique [edit | edit source]. It is performed by lightly tapping (percussing) over the nerve to elicit a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the distribution of the nerve. The Tinel sign is the tingling or prickling sensation elicited by the . It then travels under the arm close to the armpit (axilla). Improper use of crutches is a common cause of radial nerve compression at this point. Symptoms can include the following: . These can include nerve conduction studies, which test for nerve damage, or electromyography (EMG), which looks at your muscles’ electrical activity. Your radial nerve is one of five nerve branches that extend from your brachial plexus.The brachial plexus nerves start from nerves that extend from your spinal cord (nerve roots) in your lower neck (cervical spine) and upper chest (thoracic spine).They travel underneath your collarbone (clavicle) and through your armpit.. Your radial nerve starts at your lower armpit. PIN is a branch of the radial nerve that provides motor innervation to the extensor compartment. . normal tenodesis test. tenodesis test is used to differentiate from extensor tendon rupture from RA. . may help identify the level of nerve compression. may be used to rule out differential diagnoses of neuropathy. Differential.
treatment of radial nerve compression
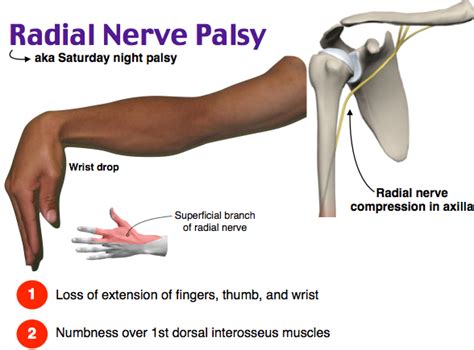
It occurs by intermittent compression on the radial nerve from the radial head to the inferior border of the supinator muscle, without obvious extensor muscle weakness. . Soames RW. A new clinical test for radial tunnel syndrome-the Rule-of-Nine test: a cadaveric study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2004; 12:83–6. [Google Scholar] Radial nerve injuries can lead to radial nerve palsy, which can cause pain and a loss of function in the arm, wrist, hands, and fingers. The most common cause of radial nerve injury is a broken arm. Radial nerve compression syndrome. This syndrome affects the radial nerve, which extends the length of the arm. It can impact wrist, hand, and finger function.Nerve compression syndromes are a common cause of nerve (neuropathic) pain in the limbs. They can lead to a pinched nerve and neuropathy (nerve damage). What are the types of nerve compression syndromes? Nerve compression syndromes can affect different peripheral nerves in your upper or lower body. Syndromes that affect your upper limbs include:
Tinel’s sign is one of the best known and widely used clinical diagnostic tools in hand surgery, plastic surgery, neurology, and orthopedics. 6 Sensory radial nerve compression symptoms may be confused with the symptoms of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis owing to pain with ulnar deviation of the wrist, and in some cases, both conditions may be present simultaneously. 3
Radial nerve compression or injury may occur at any point along the anatomic course of the nerve and may have varied etiologies. The most frequent site of compression is in the proximal forearm in the area of the supinator muscle and involves the posterior interosseous branch. . All electrodiagnostic test results are within normal limits in .
radial nerve: test thumb IP joint extension against resistence . examiner stabilizes distal radius and ulna with non-dominant hand and moves patients wrist from radial deviation to ulnar deviation, whilst applying an axial .Learn about Radial nerve dysfunction, find a doctor, complications, outcomes, recovery and follow-up care for Radial nerve dysfunction. Toggle navigation Toggle search. . The usual causes of nerve dysfunction are direct trauma, prolonged pressure on the nerve, and compression of the nerve from nearby body structures. Causes. Damage to one .
If you have symptoms of nerve compression or damage, your healthcare provider may do a simple, noninvasive test to elicit Tinel’s sign. Tinel’s sign is a tingling feeling you get when your healthcare provider taps your skin over an affected nerve. Test results can help them diagnose nerve compression so you can get treatment to relieve .The research was done in 2016 to find a more suitable diagnostic test for carpal tunnel syndrome among carpal compression test (CCT), Tinel’s test (TT), and Phalen’s test (PT). The study shows sensitivity and specificity of the Carpal compression test were higher than both Tinel's and Phalen's tests.
The radial nerve is susceptible to compression at many different locations throughout its course. Cheiralgia paresthetic is compression of the superficial branch of the radial nerve in the forearm. This condition was first described by Dr. Wartenberg in 1932 when he introduced the term cheiralgia paresthetica and reported five clinical cases.[1][2] It is also .
Radial Tunnel Syndrome:-Radial Nerve ULNT (will reproduce patient's pain in RTS, but may still have some tension present in those with LE and associated radial nerve ANTT) A test that I learned but an unfamiliar with an official name involves trying to affect the pain via compression.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the ulnar nerve at the elbow, and is the 2nd most common compression neuropathy of the upper extremity. It typically presents with paresthesias of the small and ring finger, and can be treated with both nonoperative modalities such as elbow splinting. If these fail and symptoms are severe surgical ulnar nerve .The term ‘thoracic outlet syndrome’ describes compression of the neurovascular structures as they exit through the thoracic outlet (cervicothoracobrachial region). . The pain may move laterally down the radial nerve area. Headaches are not uncommon when the upper plexus is involved. . The test is positive when paresthesia and/or . superficial branch radial nerve; dorsal digital branch; Origin: Radial nerve originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus (C5-T1) behind axillary artery; Course: Posterior wall axilla. courses on the posterior wall of the axilla (on subscapularis, latissimus dorsi, teres major) 3 Branches in axilla. posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm
The radial nerve runs from the armpit down the back of the arm to the hand. Surgery for radial nerve injury may include nerve repair, nerve graft, or nerve decompression. The radial nerve is a peripheral nerve, and it is part of a network of nerves called the brachial plexus. It provides sensation and helps move the triceps, wrist, hand, and . There are multiple compression neuropathies of the upper extremity. Some neuropathies, like carpal tunnel, are quite common; others like posterior interosseous nerve (PIN) syndrome are not.[1] Knowledge of the anatomy and function of each nerve is essential to diagnose which nerve and compression site is involved correctly. The posterior interosseous .
Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common entrapment neuropathy of the upper extremity, is caused by compression of the median nerve as it travels through the carpal tunnel. Classically, patients .

test loose brake pads

symptoms of radial nerve entrapment
WEBRenato Albani em seu quinto show solo, levanta os pontos de evolução e estagnação da sociedade, fazendo um comparativo entre passado, presente e futuro sobre os diversos conflitos que vivemos e a forma que nos comportamos frente aos fatos da vida em diversas áreas. A plateia se identifica imediatamente com os textos que são objetivos .
radial nerve compression test|radial nerve special tests